About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators Odds ratio is a measure of strength of association between risk factor and outcome/disease in a case control study It is defined as the ratio of the odds of an event70% 45% 2 After converting the odds ratio to a risk ratio, the actual risk is 14 (mortality is 14 times more likely in patients with ICU delirium compared to those without ICU delirium) Because

How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube
Odds ratio vs relative risk ratio
Odds ratio vs relative risk ratio- The difference between odds ratio and risk ratio While Risk Ratio is the probability of one thing divided by the probability of another (usually in a separated group), Odds Ratio is Odds ratios are similar to relative risks and hazard ratios, but they are different statistics Learn more about Relative Risks and Hazard Ratios How to Calculate an Odds Ratio




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect
Note that an odds ratio is a good estimate of the risk ratio when the outcome occurs relatively infrequently (The risk ratio In practice, risks and odds for a single group are not nearly as interesting as a comparison of risks and odds between two groups For risk you can make these comparisonsThe odds ratio (OR) is a ratio of 2 numbers, like the relative risk we have 3 options OR = 1 The odds in the first group are the same as those in the second So no evidence that drinking wine
Collapsibility Odds Ratios versus Risk Ratios It is known that odds ratios enjoy a certain symmetry For example, the odds ratio of outcome Y is the inverse of the odds ratio of outcomeThat is defined as p/ (1p) That is if p is the probability of the event of interest and (1p) is the probability that it doesn't happen So even from this simple case we see that the risk varies from For example, if the risk in the unexposed group is 001 and the risk in the exposed group is 005, that leads to a risk ratio of 5, but a risk difference of only 004 On the other
Percent increase = (Risk Ratio lower bound – 1) x 100 Percent decrease = (1 – Risk Ratio upper bound) x 100 It's worth stating again when comparing two proportions close to 1 orThe risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a ) For both measures a value of 1 The risk of failure with SF was 96/351 (27%) vs 32/350 (9%) with HP The RR was 3 This has a very intuitive meaning risk of failure with SF was three times more likely than HP



Q Tbn And9gcqxngysa26cxfmvxyhsfx7dcag9cllmm0xqr5nlbmujgf6lkarthl A Usqp Cau




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training
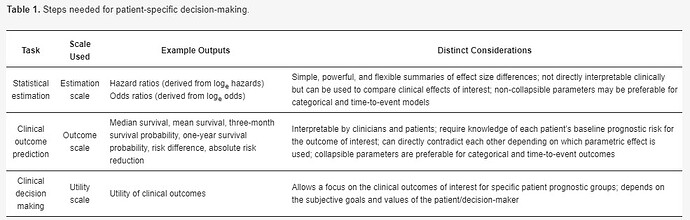
RELATIVE RISK AND ODDS RATIO The relative risk (also known as risk ratio RR) is the ratio of risk of an event in one group (eg, exposed group) versus the risk of the event in the other group Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people moreObjective Use of odds ratio (OR) in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) has been criticized because it overestimates the effect size, if incorrectly interpreted as risk ratio (RR) To




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube




What Are Cross Tables Odds Ratio And The Relative Risk Gcp Service
In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studies In For example an odds of 01 is written as 110 and an odds of 5 is written as 51 Risk and risk ratios are more commonly used than odds and odds ratios in medicine as these areShrier I, Steele R Understanding the relationship between risks and odds ratios In Corroboree Abstracts of the 13th Cochrane Colloquium;




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
To the Editor Dr Norton and colleagues 1 described significant limitations of odds ratios (ORs) but they did not report one important advantage of ORs compared with risk ratios (RRs) the Abstract The relative risk (RR) and the odds ratio (OR) are the two most widely used measures of association in epidemiology The direct computation of relative risks is feasible ifOdds and Odds Ratios Odds are the probability of an event happening / the probability of an event not happening Thus the odds of throwing a three with one die is 1/5 odds = probability /



Q Tbn And9gct4gay24i3uv90ckcbdimifr Ui3sfnfpqfzqtw4mrq21chnnb2c2zt Usqp Cau




Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj
As an extreme example of the difference between risk ratio and odds ratio, if action A carries a risk of a negative outcome of 999% while action B has a risk of 990% the relative risk is The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokers RR = (a/ (ab))/ (c/ (cd)) = (a Risk ratios At a minimum, the only change that needs to be done to get risk ratios is to change the link function that relates the mean value of the response variable to the linear




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Should One Derive Risk Difference From The Odds Ratio By S Doi Bayes Datamethods Discussion Forum
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators Odds Ratio Concept of odds The odds of an event is a ratio of the frequency (or likelihood) of its occurrence to the frequency (or likelihood) of its nonoccurrence Thus, the odds The RR is calculated as the ratio 95/85 = 117 This indicates that the risk of buying the drink is a 17% higher if we don't put the sign than if we put it It doesn't seem too much, does it?
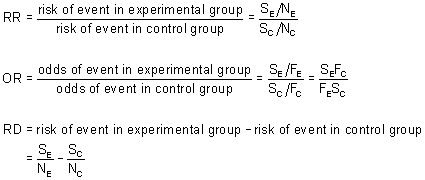



Box 9 2 A Calculation Of Rr Or And Rd




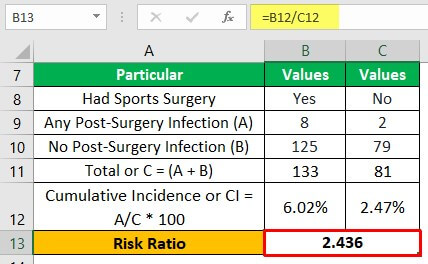
Risk Ratio Definition Formula Interpretation How To Calculate
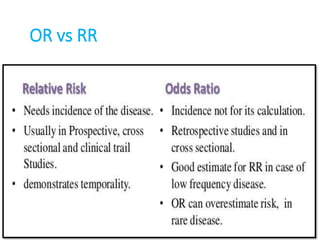
Odds Ratio The odds ratio is a measure of association between a particular exposure (suspected risk or protection factor) and a particular outcome (such as disease) It is a ratio of two odds and An RR (or OR) more than 10 indicates an increase in risk (or odds) among the exposed compared to the unexposed, whereas a RR (or OR) The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also



Risk Ratio Definition Formula Interpretation How To Calculate




Example 8 29 Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios R Bloggers
This means that in a study like this we CANNOT calculate the relative risk 2 Relative risk and odds ratio (RR in OR) The literature dealing with the relation between relative risk and odds ratio is These two measures are the odds ratio and relative risk Both are two different statistical concepts, although so much related to each other Relative risk (RR) is simply theOdds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively



Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Biostatistics Wiki Ucsf




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio
Odds ratio and risk ratios are both measure of disease effects odds ratio estimates the effects of disease based on probabilities (odds) while risk ratio is based on the risk of the event Relative Risk and Odds Ratios are both methods of comparing the likelihood of an outcome occurring between two groups The difference, and particularly the concept of odds Odds ratios While risk reports the number of events of interest in relation to the total number of trials, odds report the number of events of interest in relation to the




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube



How To Remember The Differences Between Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Likelihood Ratio And In What Instances They Should Be Applied Quora
The risk or odds ratio is the risk or odds in the exposed group divided by the risk or odds in the control group A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk orInstead we can calculate the odds ratio for vaccination to assess the association between vaccination and infection The odds that an infected subject was vaccinated are / =16/30=053 For example, if survival is 50% in one group and 40% in another, the measures of effect or association are as follows the risk ratio is 050/040 = 125 (ie, a relative increase in




Odds Ratio And Relative Risk




Epidemiology Odds Ratio Or Bean Around The World
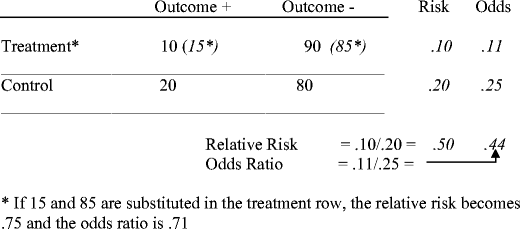
EXAMPLE Calculating Odds Ratios Use the data in Table 315 to calculate the risk and odds ratios Risk ratio 50 ⁄ 10 = 50 Odds ratio (100 × 7,9) ⁄ (1,900 × 80) = 52 Notice that the odds ratioThe difference between odds and risk is small when the event is rare (as illustrated in the first example above where a risk of 0091 was seen to be similar to an odds of 01) When events are When the outcome is not rare in the population, if the odds ratio is used to estimate the relative risk it will overstate the effect of the treatment on the outcome measure The odds




Odds Ratio Calculation And Interpretation Statistics How To



Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Evaluation
The odds of a bad outcome with the existing treatment is 02/08=025, while the odds on the new treatment are 01/09=0111 (recurring) The odds ratio comparing the newEnglishwise, they are correct it is the odds and the odds are based on a ratio calculation It is not , however, the odds ratio that is talked about when results are reported The odds ratio when




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Risk Ratio Versus Odds Ratio Dr Journal Club




A Most Odd Ratio Interpreting And Describing Odds Ratios Abstract Europe Pmc
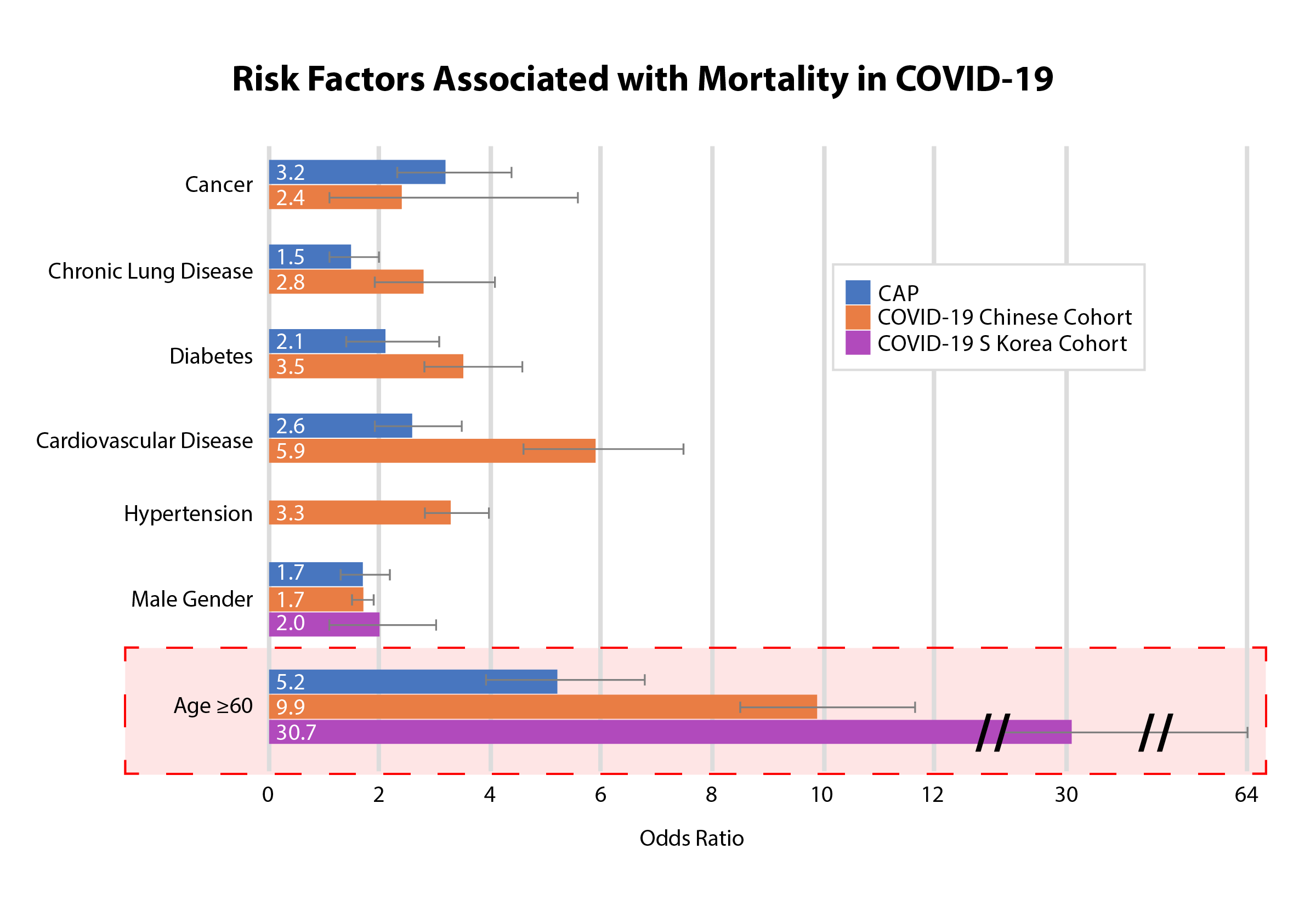



Nnt Review Odds Ratios Of Mortality Risk Factors




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Kevin Whelan If You Re Struggling With Odds Ratios Relative Risks Standardised Mean Differences And Number Needed To Treat And The Associated Alphabet Soup Or Rr Smd Nnt Then This Paper




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect
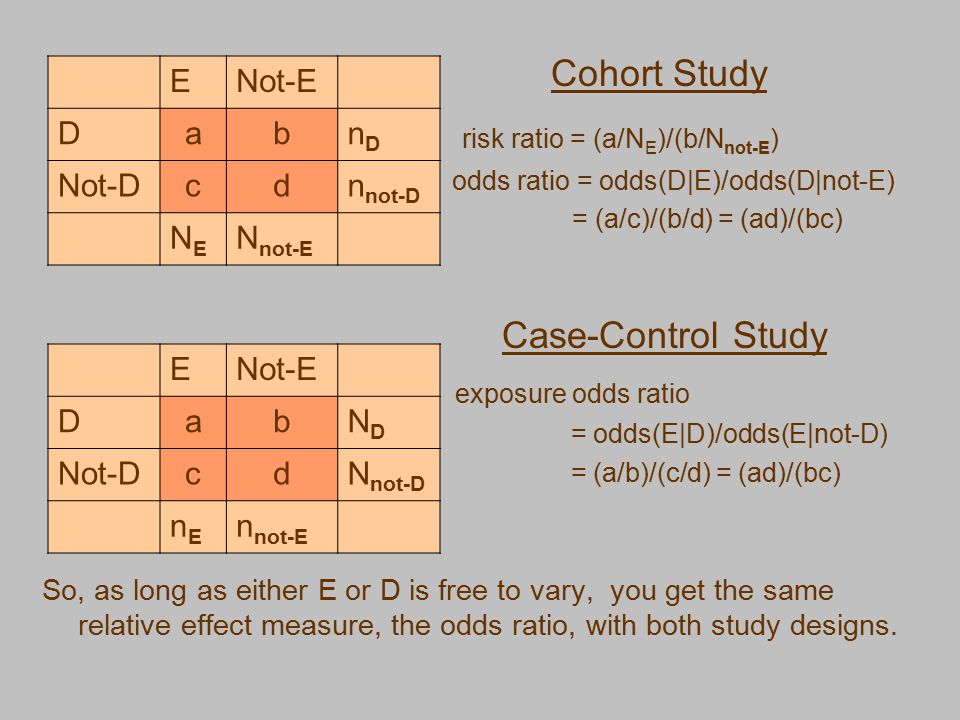



Case Control Studies Statistical Analysis Ppt Video Online Download




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk




How To Calculate An Odds Ratio Youtube




Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk What S The Difference Statology




Calculation And Interpretation Of Risk Difference Rd Relative Risk Download Scientific Diagram
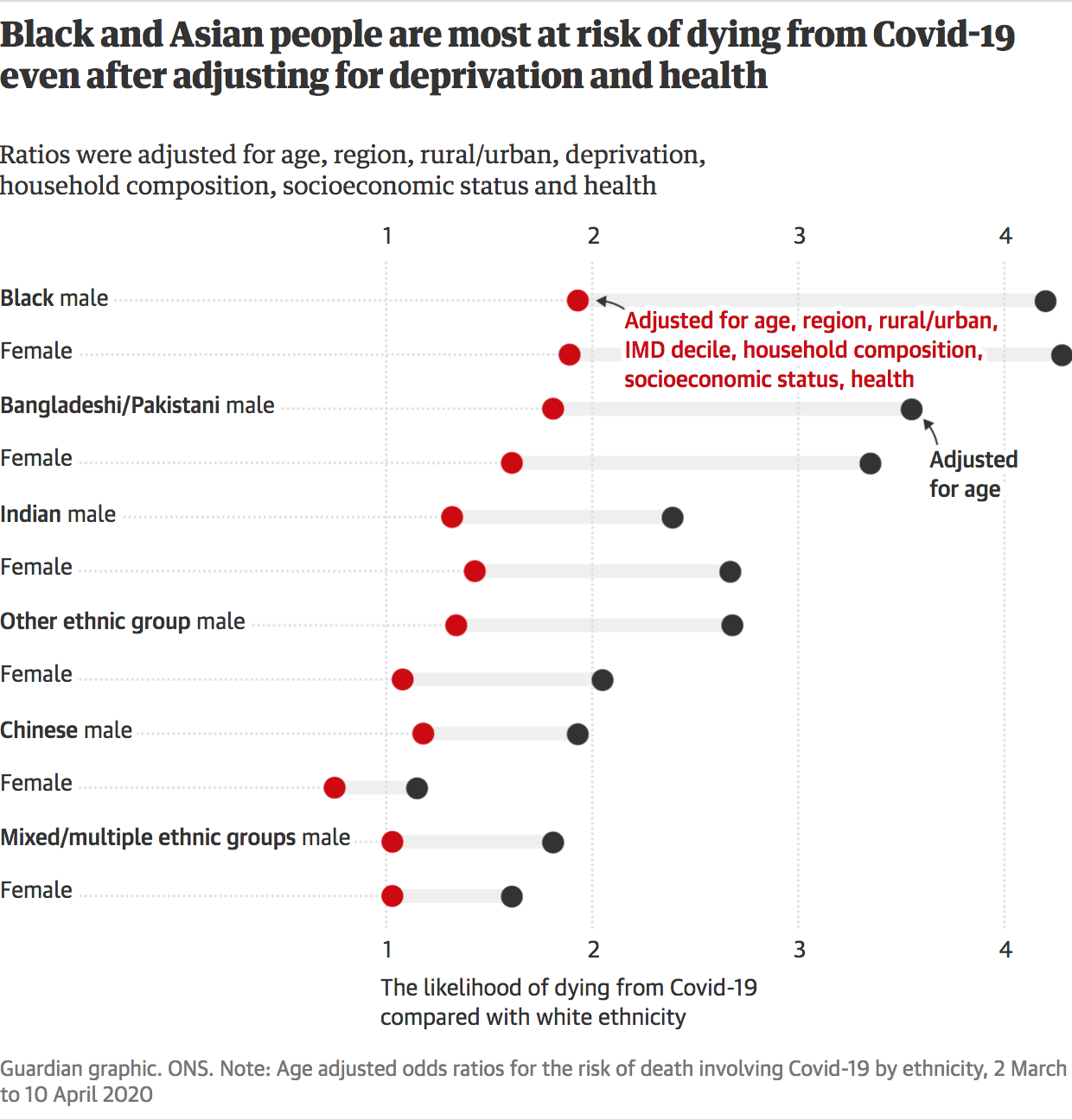



Against All Odds How To Visualise Odds Ratios To Non Expert Audiences Henry Lau



Requesting Effect Measures



Tips For Teachers Of Evidence Based Medicine Understanding Odds Ratios And Their Relationship To Risk Ratios Springerlink



File Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio Svg Wikimedia Commons




Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough




The Relationship Between Nnt Calculated From An Odds Ratio Or And An Download Scientific Diagram




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




Pdf Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk For Cross Sectional Data Semantic Scholar




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean
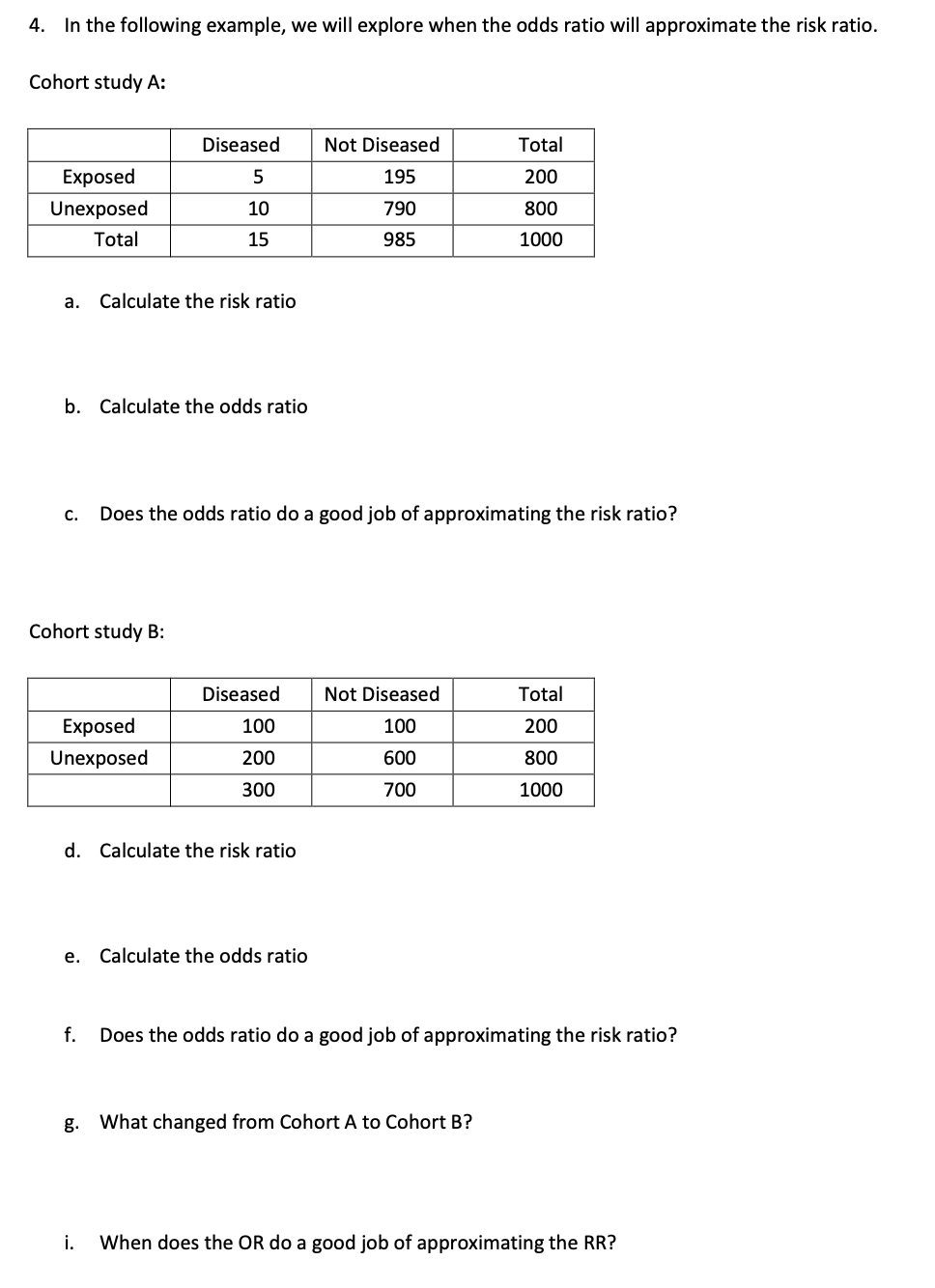



Solved 4 In The Following Example We Will Explore When The Chegg Com
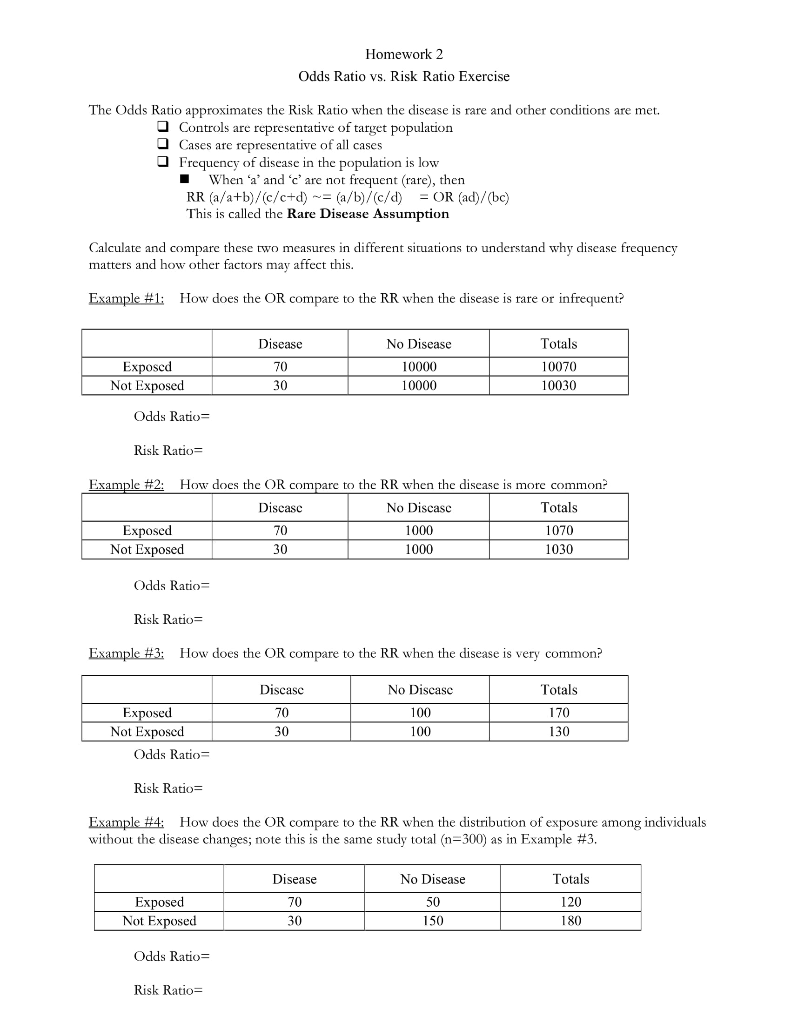



Solved Homework 2 Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Exercise The Chegg Com
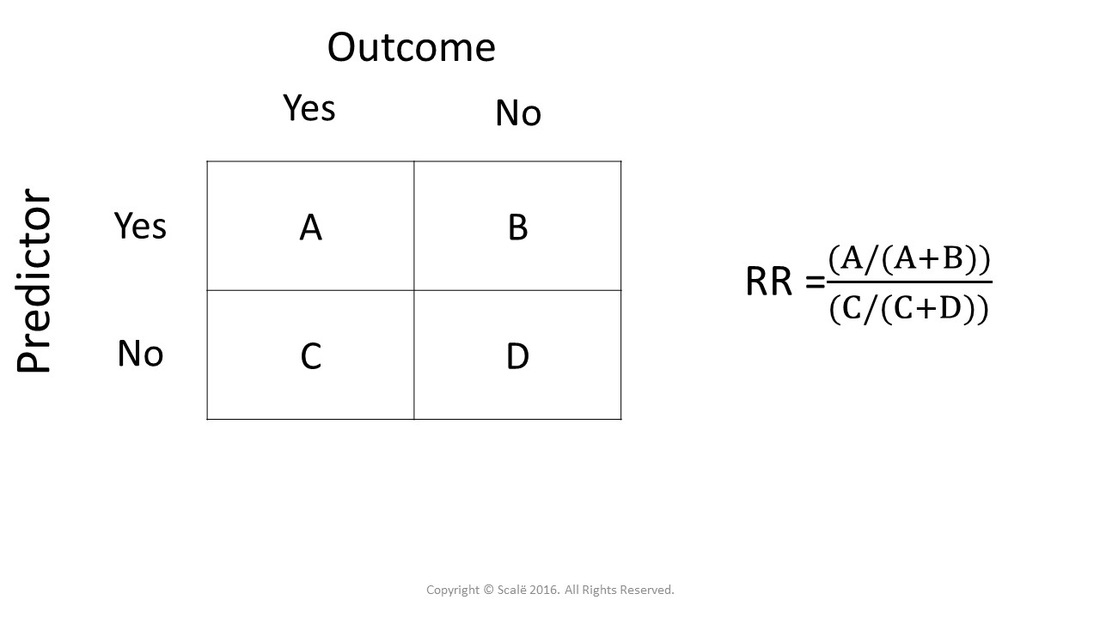



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




Jussi Tervola Twitter પર Nice Graph Depicting The Relationship Between Odds Ratio And Relative Risk T Co Lssoq7tqmd T Co Cqpgzysd8w Twitter




Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk What S The Difference Statology



2




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Hazard Ratio Vs Relative Risk Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Show Background Cpb Presentation Graphics Presentation Powerpoint Example Slide Templates



Rr Relative Risk Vs Or Odds Ratio Dr Venugopala Rao Manneni



Img054 Jpg



Q Tbn And9gcr9krg8lapks7gfw8dtldgga6yea7i0fjo7qe4sh Vhwxscnjdtfdjh Usqp Cau




1 The Odds Ratio Relative Odds In A Case Control Study We Do Not Know The Incidence In The Exposed Population Or The Incidence In The Nonexposed Population Ppt Download




Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Controversy And Debate Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research Paper 4 Odds Ratios Are Far From Portable A Call To Use Realistic Models For Effect Variation In




Lago Titicaca Elegante Escucho Musica Relative Risk Calculation Formula Maquina De Escribir Infectar Raro
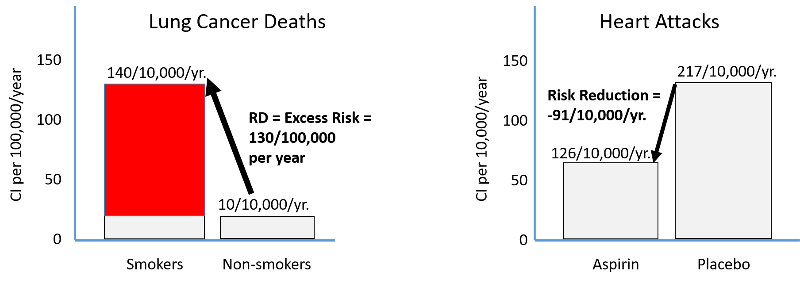



Risk Ratio And Risk Difference
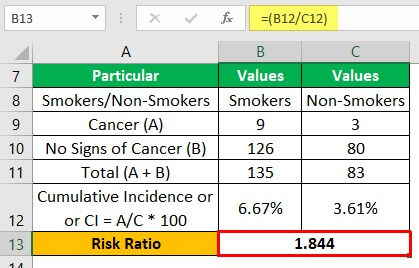



Risk Ratio Definition Formula Interpretation How To Calculate
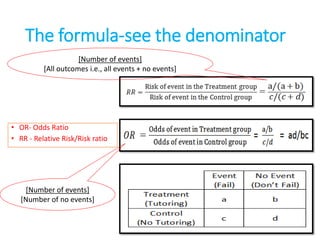



Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Evaluation
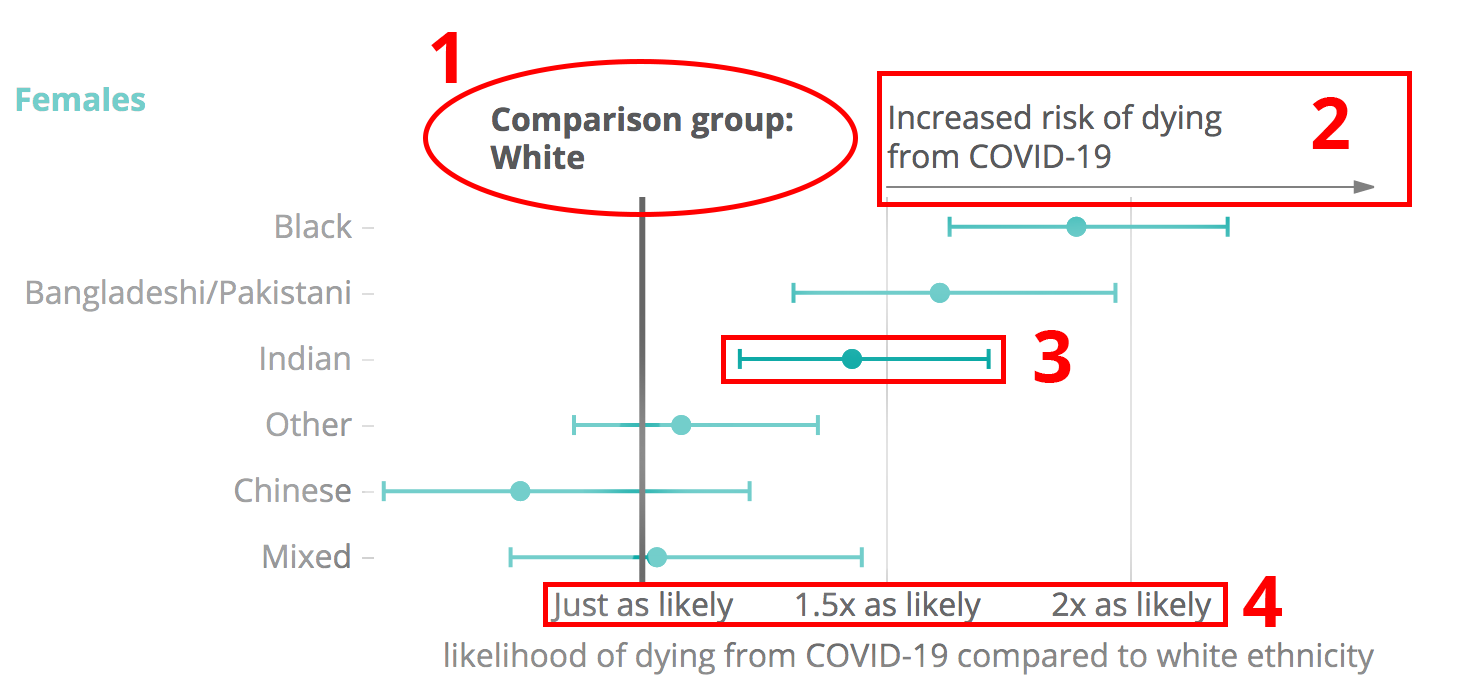



Against All Odds How To Visualise Odds Ratios To Non Expert Audiences Henry Lau




Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio For Cardiovascular Disease Incidence Download Scientific Diagram




Hazard Ratio Odds Ratio Relative Risk Hr Or Rr Or Adverse Effects Download Scientific Diagram




Interpretation Of Odds And Risk Ratios O Connor 13 Journal Of Veterinary Internal Medicine Wiley Online Library
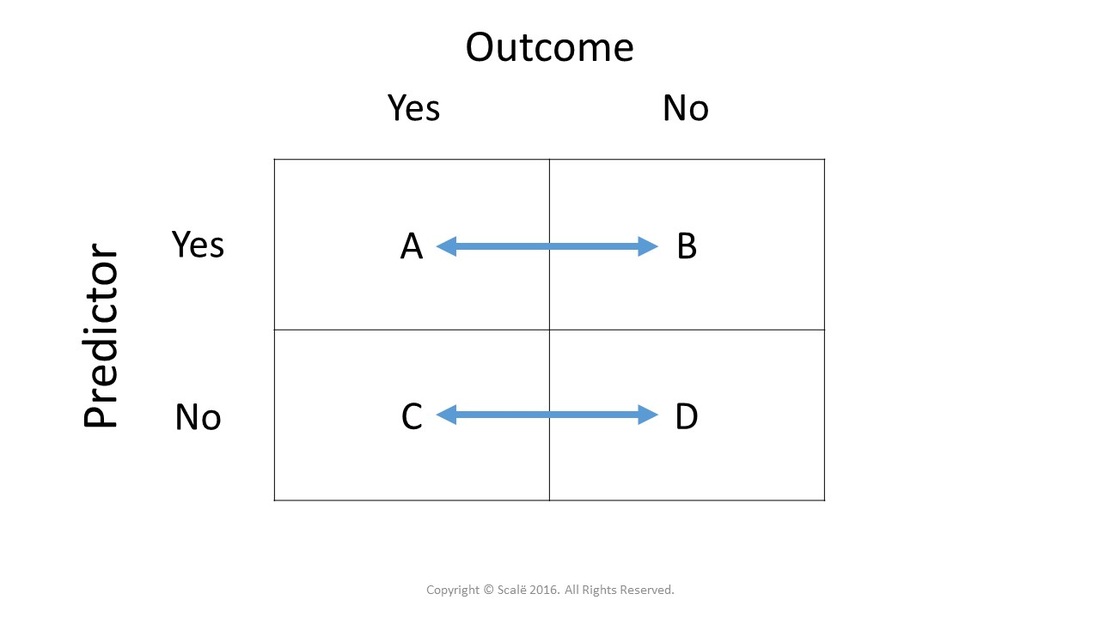



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals
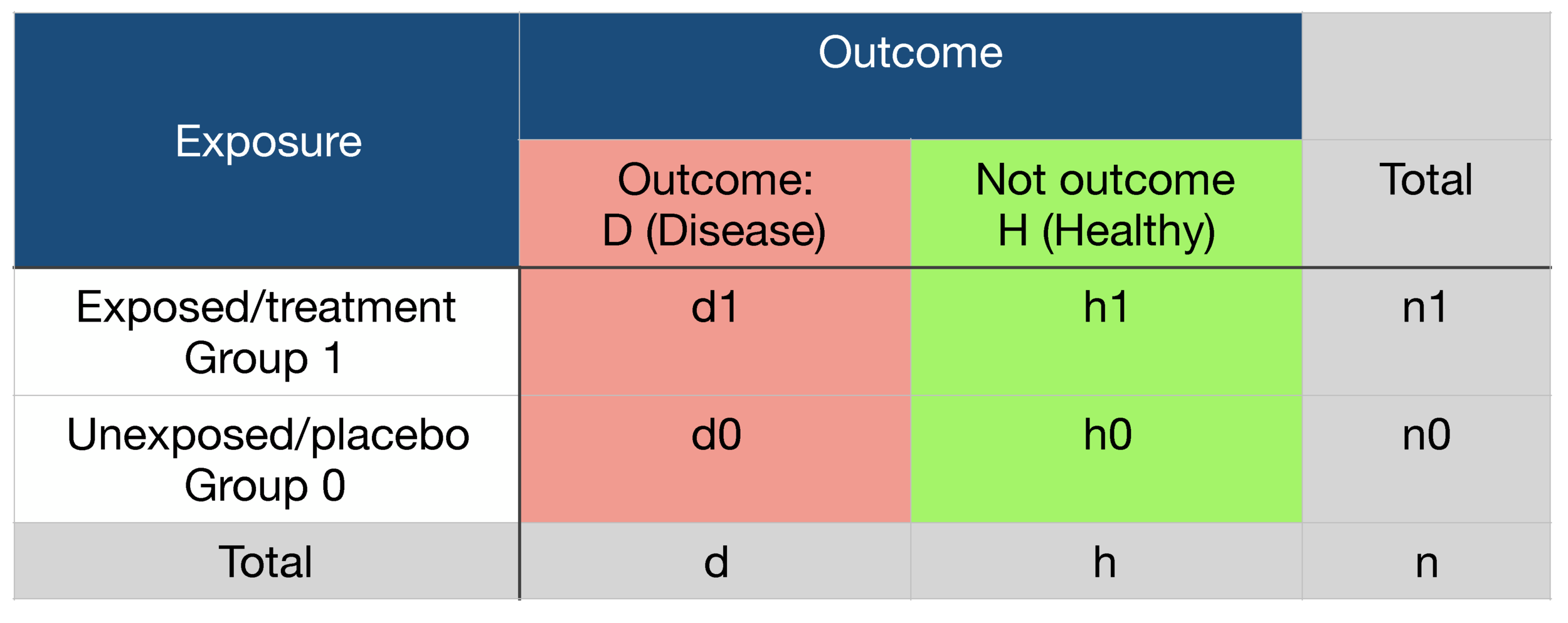



Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gpraj




Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk



Q Tbn And9gct4gay24i3uv90ckcbdimifr Ui3sfnfpqfzqtw4mrq21chnnb2c2zt Usqp Cau




View Image




1 A Comparison Of Odds Ratio And Risk Ratio With The Average Marginal Download Scientific Diagram




Relative And Atribute Risk




Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube




Mixing Of Confounding And Non Collapsibility A Notable Deficiency Of The Odds Ratio American Journal Of Cardiology




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube




Community Medicine Odds Ratio Relative Risk Attributable Risk Population Attributable Risk




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar



Relative Risk And Odds Ratios Categorical Data And Chi Square Tests Biostatistics For The Health Sciences




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated




Understanding Odds Ratios Sainani 11 Pm Amp R Wiley Online Library




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals
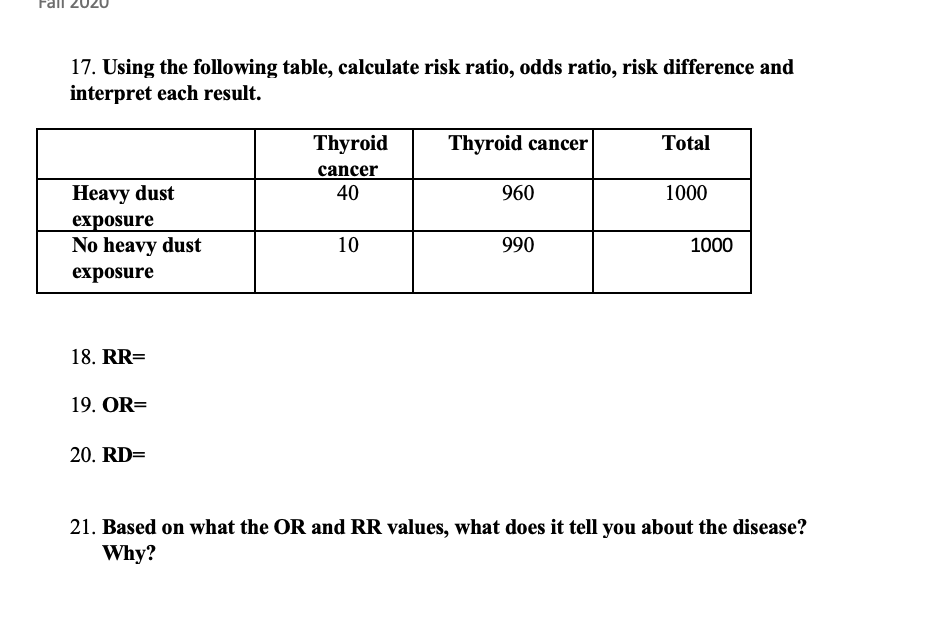



Fall 17 Using The Following Table Calculate Risk Chegg Com
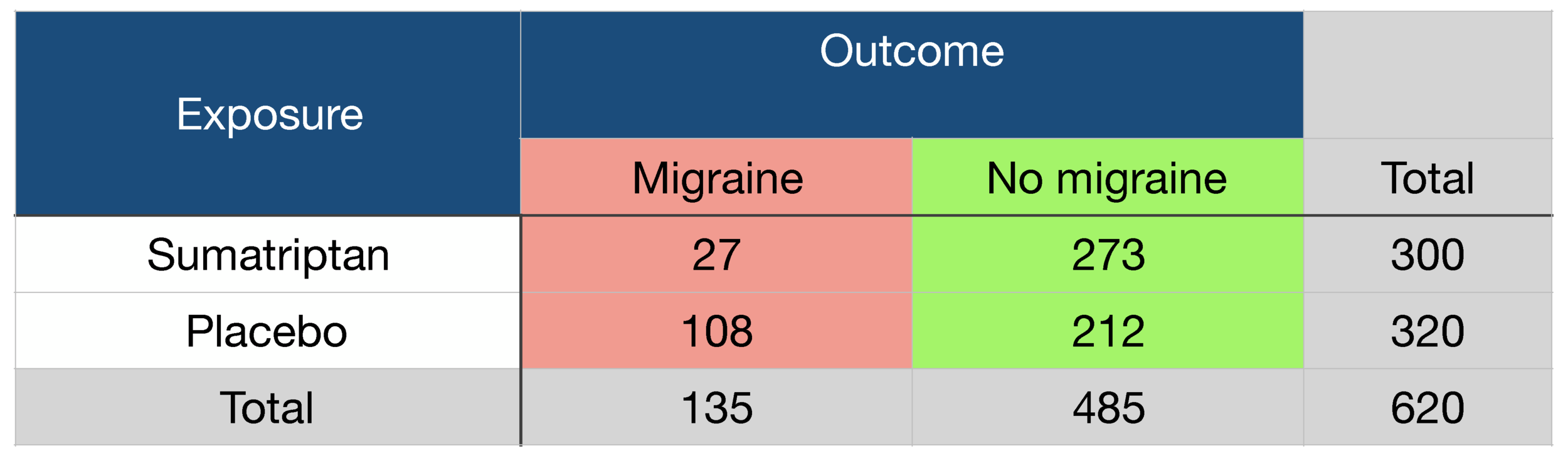



Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gpraj




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios



Img009 Gif




Calculation Of Odds Ratios Or And Relative Risk Rr Derived From Download Scientific Diagram
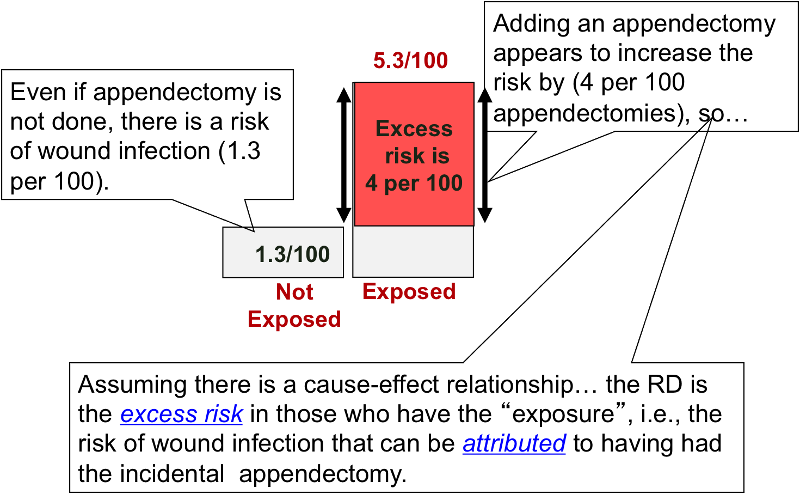



Risk Differences And Rate Differences



Odds Ratio Relative Risk Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Model Example Cpb Presentation Graphics Presentation Powerpoint Example Slide Templates
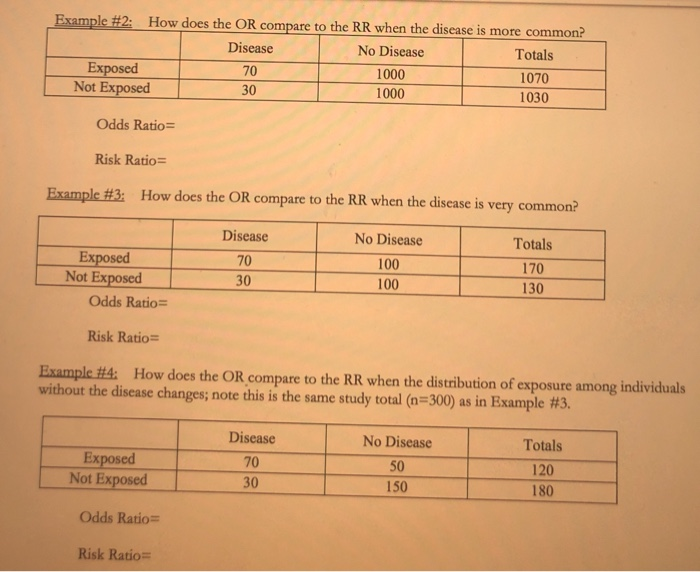



Solved Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Exercise The Odds Ratio Chegg Com




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated




Table 2 From Interpretation Of Odds And Risk Ratios Semantic Scholar




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube
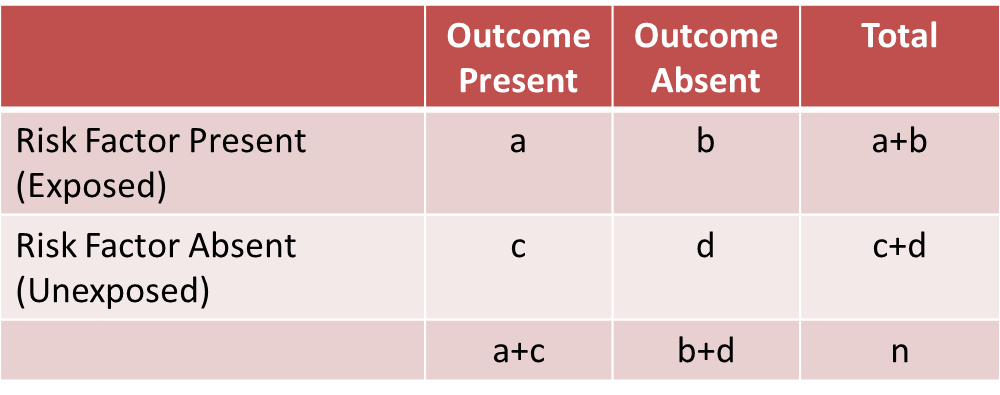



A Stratified Analysis




P S Is Odds Ratio And Risk Ratio The Same Thing The Definition I Ve Seen Are Pretty Similar R Mcat




Math3010 Week 6



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿